 [AED023] Inserting an element on a given position
[AED023] Inserting an element on a given positionIn what concerns the continuous evaluation solving exercises grade during the semester, you should submit until 23:59 of November 9th
(this exercise will still be available for submission after that deadline, but without couting towards your grade)
[to understand the context of this problem, you should read the class #05 exercise sheet]
 [AED023] Inserting an element on a given position
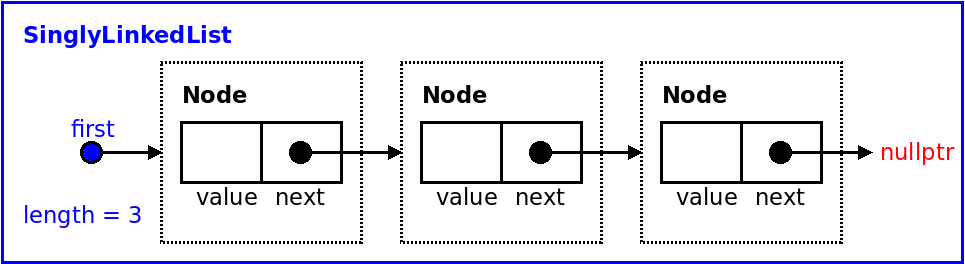
[AED023] Inserting an element on a given positionIn this problem you should only submit a singlyLinkedList.h file with a self-containing definition of a class SinglyLinkedList<T>
Use as a basis the class SinglyLinkedList<T> (see code | download code) which implements a generic singly linked list similar to what was done on classes, with methods to add and remove an element in the end, return the size, knowing if the list is empty or printing the list.
Add a new method void insert(int pos, const T & v) to the class. The function should insert element with value v right before position pos (with the positions starting in zero). If pos is invalid and not between 0 and length then the method should do nothing. Note that inserting at position length should mean adding at the last position (right before nullptr).
You should submit the file singlyLinkedList.h with the method insert added to SinglyLinkedList<T> as requested (and without removing any of the other existing methods). You can however create additional methods, if you need them.
Mooshak will use the following code to link to your class, read the inputs, build the lists and call your method, printing its result.
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include "singlyLinkedList.h" // Read n and then n elements to add to the list using addFirst, followed by // Read q and then q queries pos val to call insert(pos,val) template <typename T> void read() { int n; std::cin >> n; SinglyLinkedList<T> lst; for (int i=0; i<n; i++) { T v; std::cin >> v; lst.addFirst(v); } std::cout << "lst = " << lst.toString() << " | size = " << lst.size() << std::endl; std::cin >> n; for (int i=0; i<n; i++) { int pos; T v; std::cin >> pos >> v; std::cout << "lst.insert(" << pos << "," << v << ")" << std::endl; lst.insert(pos, v); std::cout << "lst = " << lst.toString() << " | size = " << lst.size() << std::endl; } std::cout << "-------------------------" << std::endl; } int main() { int n; std::cin >> n; for (int i=0; i<n; i++) { std::string type; std::cin >> type; if (type == "int") read<int>(); else if (type == "char") read<char>(); else if (type == "string") read<std::string>(); } return 0; }
| Example Input | Example Output |
3 int 1 1 5 0 2 2 3 4 4 1 5 2 6 char 4 a b c d 5 4 z 0 y -1 x 10 w 1 v string 0 2 0 hello 1 world |
lst = {1} | size = 1
lst.insert(0,2)
lst = {2,1} | size = 2
lst.insert(2,3)
lst = {2,1,3} | size = 3
lst.insert(4,4)
lst = {2,1,3} | size = 3
lst.insert(1,5)
lst = {2,5,1,3} | size = 4
lst.insert(2,6)
lst = {2,5,6,1,3} | size = 5
-------------------------
lst = {d,c,b,a} | size = 4
lst.insert(4,z)
lst = {d,c,b,a,z} | size = 5
lst.insert(0,y)
lst = {y,d,c,b,a,z} | size = 6
lst.insert(-1,x)
lst = {y,d,c,b,a,z} | size = 6
lst.insert(10,w)
lst = {y,d,c,b,a,z} | size = 6
lst.insert(1,v)
lst = {y,v,d,c,b,a,z} | size = 7
-------------------------
lst = {} | size = 0
lst.insert(0,hello)
lst = {hello} | size = 1
lst.insert(1,world)
lst = {hello,world} | size = 2
-------------------------
|